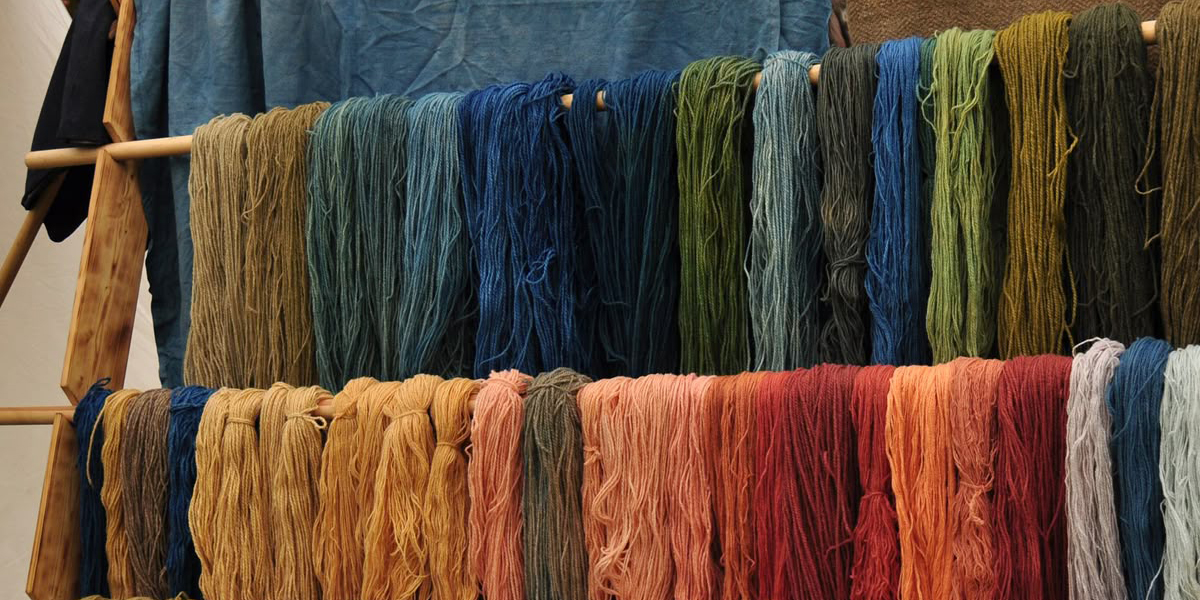
Fiber dyed fabrics undergo a process where fibers get dyed before being spun into yarn, resulting in vibrant colors throughout the fabric. In contrast, yarn dyed fabric involves dyeing the yarns prior to weaving or knitting, which allows for intricate patterns and color combinations. This technique is particularly suitable for items like school uniform yarn dyed fabric. Additionally, eco-friendly fiber dyed fabric is gaining popularity for its sustainable qualities, while fiber dyed fabric for pants offers a unique aesthetic. Ultimately, when considering the best quality of suiting fabric, both fiber dyed and yarn dyed options present distinct advantages. So, what are the differences between fiber dyed and yarn dyed? Each method has its own unique benefits that cater to various textile needs.
Key Takeaways
- Fiber dyed fabrics offer vibrant colors that penetrate deeply into the fibers, ensuring long-lasting hues and exceptional colorfastness.
- Yarn dyed fabrics allow for intricate patterns and designs, making them ideal for stylish clothing and home decor.
- Choosing eco-friendly fiber dyed fabrics can reduce water usage and chemical waste, contributing to a more sustainable textile industry.
Overview of Dyeing Methods
Definition of Fiber Dyeing
Fiber dyeing is a process where the raw fibers are dyed before they are spun into yarn. This method allows for deep and vibrant colors to penetrate the fibers, resulting in a rich hue throughout the fabric. The process typically involves several steps, including fabric inspection, batching, and pretreatment, followed by the actual dyeing. I find that this method is particularly effective for achieving uniform color, especially in fabrics that require a solid color finish.
Here’s a quick overview of the fiber dyeing process:
- Fabric received from batching section
- Grey fabric inspection
- Batching
- Turning
- Sewing
- Fabric loading
- Pretreatment (Scouring & Bleaching)
- The enzyme (Antipilling)
- Dyeing
- Washing
- Fixing
- Softening/Finishing
- Unloading the dyed fabric
Definition of Yarn Dyeing
Yarn dyeing, on the other hand, involves dyeing the yarns before they are woven or knitted into fabric. This technique allows for intricate patterns and color combinations, making it ideal for creating designs that require multiple colors. I appreciate how yarn dyeing can produce unique textures and visual effects that are not achievable with fiber dyeing. The process includes methods like hank dyeing, where loose yarn is soaked in dye, and slasher dyeing, which is more suitable for large-scale production.
What are the differences between fiber dyed and yarn dyed?
When I explore the differences between fiber dyed and yarn dyed fabrics, the dyeing process stands out as a primary factor.
Dyeing Process
The dyeing process for these two types of fabrics varies significantly. In fiber dyeing, the dyeing occurs at the fiber stage before they are spun into yarn. This method is also known as stock dyeing. On the other hand, yarn dyeing happens after the yarn is spun but before it is woven into fabric. This process often employs methods like hanks or package dyeing.
Here’s a quick comparison of the dyeing processes:
| Dyeing Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Fiber Dyeing | Dyeing occurs at the fiber stage before they are spun into yarn, also known as stock dyeing. |
| Yarn Dyeing | Dyeing happens after the yarn is spun but before it is woven into fabric, using methods like hanks or package dyeing. |
The machinery used for each dyeing type also differs. Fiber dyeing requires various fiber dyeing machines that convert fiber to yarn, effectively dyeing the fiber molecules in both natural and manmade fibers. In contrast, yarn dyeing utilizes hank and package dyeing machines, which create color patterns in woven fabric.
| Type of Dyeing | Machinery Used | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Dyeing | Various fiber dyeing machines | Converts fiber to yarn, dyeing fiber molecules in natural and manmade fibers. |
| Yarn Dyeing | Hank and Package dyeing machines | Used for yarns intended for yarn-dyed fabric and knit fabric, creating color patterns in woven fabric. |
Colorfastness Comparison
Colorfastness is another critical difference between fiber dyed and yarn dyed fabrics. I have observed that yarn-dyed fabrics often exhibit better lightfastness than fiber-dyed fabrics. The dyeing method significantly influences the overall colorfastness of the fabric.
Here’s a breakdown of how these two types compare:
| Fabric Type | Light Fastness | Wash Fastness |
|---|---|---|
| Yarn-dyed | Better | Varies |
| Fiber-dyed | Generally worse | Varies |
In my experience, yarn-dyed fabrics typically have superior light fastness compared to fiber-dyed fabrics. However, the wash fastness of both types can differ based on the dyeing process and the dyes used. Standardized tests, such as those outlined in the ISO and AATCC standards, measure colorfastness effectively.
| Test Type | ISO Standard | AATCC Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Color Fastness to Washing | ISO 105 C06 | AATCC 61 |
| Color Fastness to Crocking | ISO 105 X12 | AATCC 8 |
| Color Fastness to Light | ISO 105 B02 | AATCC 16 |
| Color Fastness to Perspiration | ISO 105 E04 | AATCC 15 |
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of fiber dyeing versus yarn dyeing is another area where I see notable differences. Fiber dyeing generally requires significant chemicals for preactivation and dyeing, especially reactive dyes and auxiliaries. This results in large volumes of wastewater with high chemical oxygen demand (COD) and biochemical oxygen demand (BOD).
In contrast, yarn dyeing typically uses fewer chemicals and produces less wastewater with lower chemical contamination. The water consumption for fiber dyeing is also high, approximately 230 to 270 tons per ton of textile material, while yarn dyeing consumes less water.
| Aspect | Fiber Dyeing | Yarn Dyeing |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Usage | Requires significant chemicals for preactivation and dyeing, especially reactive dyes and auxiliaries. | Generally uses fewer chemicals compared to fiber dyeing. |
| Effluent Output | Generates large volumes of wastewater with high COD and BOD due to the chemicals used. | Produces less wastewater with lower chemical contamination. |
| Water Consumption | High water usage, approximately 230 to 270 tons per ton of textile material. | Lower water usage compared to fiber dyeing. |
Benefits of Fiber Dyed Fabrics
Color Vibrancy
One of the standout benefits of fiber dyed fabrics is their exceptional color vibrancy. I have noticed that the dye penetrates the fibers deeply, resulting in rich and lasting colors. This method ensures that the color remains integral to the fiber, which leads to several advantages:
- Exceptional Colorfastness: The colors resist fading under harsh conditions, including sunlight and washing.
- Long-lasting Vibrancy: Even with exposure to chemicals, the colors maintain their brilliance.
- Consistency Across Batches: I appreciate that manufacturers can produce up to one million meters of fabric without color differences, ensuring uniformity in large orders.
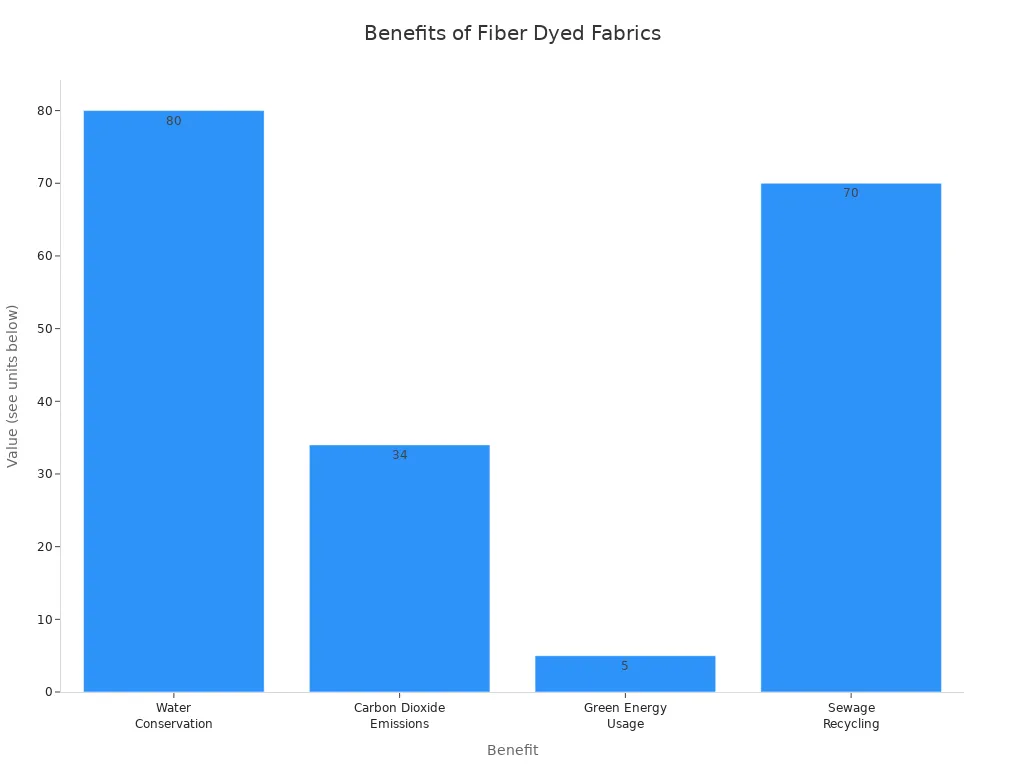
Here’s a quick comparison of the benefits of fiber dyed fabrics versus normal dyed fabrics:
| Benefit | Fiber Dyed Fabrics | Normal Dyed Fabrics |
|---|---|---|
| Water Conservation | 80% more saving | N/A |
| Carbon Dioxide Emissions | 34% less | N/A |
| Green Energy Usage | 5 times more | N/A |
| Sewage Recycling | 70% | N/A |
Eco-friendliness
I find fiber dyed fabrics to be significantly more eco-friendly than other dyeing methods. The use of eutectic solvents in the dyeing process greatly reduces water usage. This efficiency not only conserves natural resources but also contributes to a lower carbon footprint. Here are some key points that highlight their eco-friendliness:
- Improved dye-fiber interactions lead to better dye uptake and efficiency.
- Enhanced colorfastness indicates a longer lifespan for the fabric, reducing the need for re-dyeing.
- Sustainable fibers, such as solution-dyed fabrics, require less water and energy during production.
By choosing fiber dyed fabrics, I feel I am making a responsible choice that benefits both the environment and the quality of the textiles I use.
Benefits of Yarn Dyed Fabrics
Design Versatility
Yarn dyed fabrics offer remarkable design versatility that I find particularly appealing. The process of dyeing individual yarns before weaving allows for intricate designs that are hard to achieve with other methods. Here are some key aspects of this versatility:
- Intricate Patterns: Yarn dyeing enables the creation of complex patterns such as stripes, checks, and jacquards. This variety allows designers to explore diverse styles and aesthetics.
- Color Combinations: The method supports a vast array of colors, making it easy to incorporate contrasting elements or monochromatic schemes. This enhances visual interest and creativity in textile design.
- Unique Textures: Different dyeing techniques, like immersion and space dyeing, contribute to unique textures and appearances. I appreciate how these variations can elevate the overall look of a fabric.
The labor-intensive nature of yarn dyeing also supports traditional textile techniques and local economies, which I find commendable.
Durability
Durability is another significant benefit of yarn dyed fabrics. I have noticed that these fabrics maintain their shape and size better over time, contributing to the longevity of the product. Here’s why durability stands out:
- Color Fastness: Yarn-dyed products exhibit superior color fastness compared to printed fabrics. The dye penetrates deeply into the fibers, ensuring that colors remain vibrant throughout multiple washes and usage cycles.
- Resistance to Fading: Yarn-dyed fabrics are less prone to fading and discoloration. They retain their bright color and beautiful appearance for a long time, which is especially important for high-end clothing and home textiles.
- Long-Term Use: Because the dye is better fixed inside the fiber, yarn-dyed fabrics are ideal for products that require frequent washing. This enhances their longevity while reducing the decline in beauty due to fading.
In my experience, choosing yarn dyed fabrics means investing in quality and style that lasts.
Typical Applications
Common Uses for Fiber Dyed Fabrics
Fiber dyed fabrics find their place in various applications across the apparel and home textile industries. I often see these fabrics used in luxury textiles, such as silk scarves and wool suits, where vibrant colors enhance the overall aesthetic. Here’s a breakdown of some common applications:
| Application Type | Examples |
|---|---|
| Luxury Textiles | Silk scarves, wool suits, high-end fashion |
| Carpeting & Upholstery | Nylon-based fibers |
| Specialty Dyed Leather Goods | |
| Apparel Dyeing | T-shirts, jeans, casual wear |
| Home Textiles | Bedding, towels, upholstery |
| Fashion Industry | High-end colored cotton fabrics |
| Low-Cost Textiles | Towels, tablecloths, budget-friendly apparel |
| Industrial Textiles | Automotive interiors, outdoor furniture |
| Polyester Apparel | Athleisure, leggings, sportswear |
| Activewear | Performance fabrics |
I appreciate how fiber dyed fabrics cater to both high-end and budget-friendly markets, making them versatile for various consumer needs.
Common Uses for Yarn Dyed Fabrics
Yarn dyed fabrics are prevalent in the clothing and apparel category, which accounted for over 51% of the textile dyes market in 2023. I find this method particularly useful for creating intricate designs and patterns. Here are some common uses for yarn dyed fabrics:
- Shirts and Blouses: The ability to create stripes and checks makes yarn dyed fabrics ideal for stylish shirts.
- Home Decor: I often see these fabrics used in curtains and upholstery, where their durability and colorfastness shine.
- Sportswear: The performance characteristics of yarn dyed fabrics make them suitable for activewear, ensuring they withstand rigorous use.
In my experience, both fiber dyed and yarn dyed fabrics serve distinct purposes, each offering unique benefits that cater to different market segments.
In summary, fiber dyed fabrics excel in color vibrancy and eco-friendliness, while yarn dyed fabrics offer durability and design versatility. I encourage you to explore these dyeing methods further. Understanding their unique benefits can enhance your choices in textiles, especially when considering factors like colorfastness and sustainability.
Post time: Oct-11-2025